Consequences

Bladder, kidney and bowel problems
Spina Bifida is a neurological system disorder and therefore affects vital functions of the gastro-urinary system.
Various bladder dysfunctions lead to different forms of incontinence, which must also be treated differently. Medication, bladder surgery and catheterization are the most common treatment procedures for people with bladder disorders.
Correct treatment of bladder dysfunctions ensures that kidney function is kept as intact as possible so that the kidneys can continue to function normally.
Unfortunately, for many people with Spina Bifida, kidney function is also impaired due to pressure on the kidneys from the bladder.
Normal bowel function with regular bowel movements is also ruled out for many people with spina bifida. Adapted nutrition (high fiber), bowel irrigation and surgery are common treatment methods to promote regular defecation.
Lower limbs
Deformities can occur at the level of the feet, lower legs and pelvis as a result of motor (movement), neurological (nerve supply) and sensory (feeling) problems.
Where walking is possible, orthopedic shoes, braces or a parapodium can be helpful, sometimes in combination with orthopedic surgery on the lower limbs.
A wheelchair with or without a custom seating shell or adapted footrests is the only way for many people with Spina Bifida to move under their own power. It is therefore important to be quite critical when choosing a wheelchair.
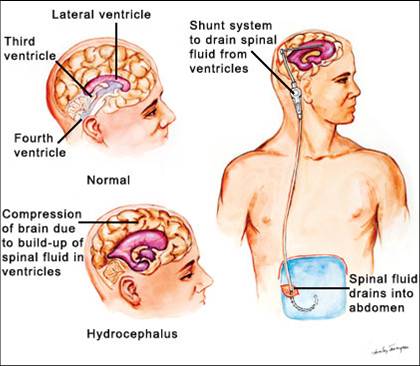
Neurological problems
Hydrocephalus (water on the brain)
Correction by: surgical procedure / shunt ETV
Epilepsy
Correction by: medication
Arnold-Chiari malformation
Correction by: surgical procedure
Tethered Cord
Correction by: surgical procedure
Psycho-social dysfunction
1. High care needs: has financial implications, requires informal care organization
2. Frequent hospitalization: leads to hospitalism
3. School issues: integration into mainstream education is not always straightforward, adapted forms of education, not always in the immediate vicinity
